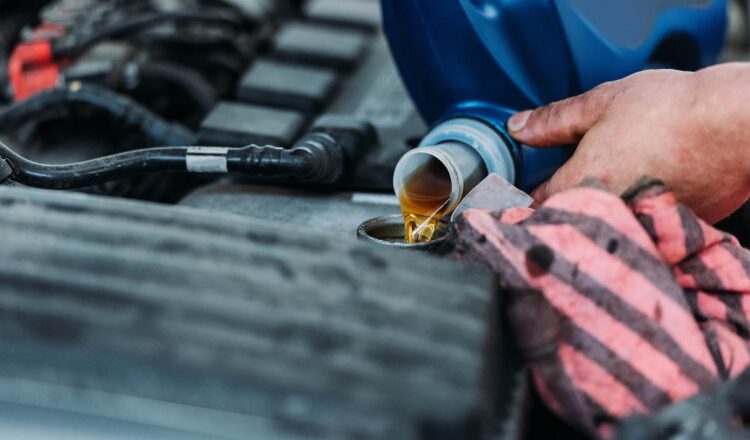
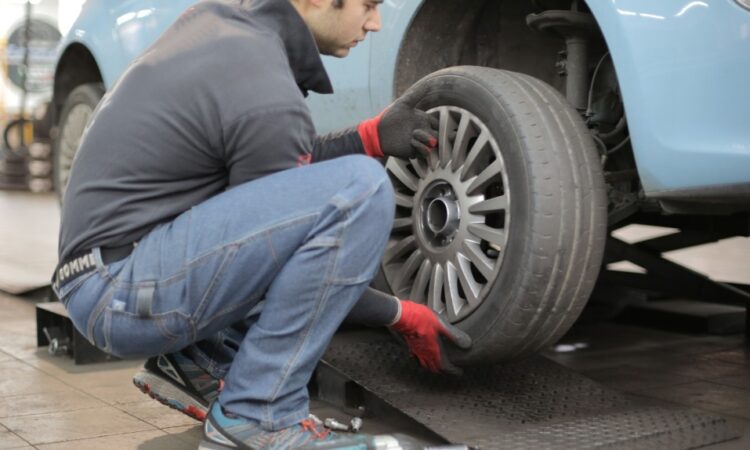
Changing the engine oil is an indispensable aspect of vehicle maintenance, essential for ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. While professional workshops are available to carry out this procedure, many car owners opt for the do-it-yourself (DIY) method. However, before delving into this task, it is crucial to consider the environmental and legal implications associated with the used oil. This introduction sets the stage for understanding the intricacies of the oil change process, emphasizing the need for conscientious actions and responsible disposal methods. It reveals the legal obligations surrounding oil changes, the environmental impact of improper practices, and the importance of selecting appropriate locations for this fundamental automotive maintenance procedure. As we navigate through the subsequent sections, we will unravel the complexities of oil changes, exploring the legal, environmental, and practical dimensions that contribute to a holistic understanding of this essential automotive process.
Legal and Environmental Considerations
Performing an engine oil change extends beyond the confines of the garage; it carries legal and environmental responsibilities that demand meticulous attention. Understanding these considerations is paramount for conscientious car owners.

- Legal Obligations:
Carrying out an oil change is not a casual affair, and it cannot be executed haphazardly in any location. Legal regulations explicitly prohibit changing oil in public spaces, such as parking lots, underscoring the need for a designated area. This restriction is not just a matter of convenience; it’s a legal requirement aimed at preventing environmental harm. Violating these regulations could lead to fines, with penalties potentially reaching up to PLN 1,500. Moreover, if a leaking vehicle is deemed responsible for environmental damage, the authorities may take more severe measures, including the revocation of the vehicle’s registration certificate. - Environmental Impact:
Oil, albeit a common automotive fluid, is highly toxic and poses a substantial threat to the environment. Even a small quantity of spilled oil can contaminate water sources, causing significant ecological damage. Recognizing the environmental consequences of improper oil disposal is crucial. Beyond legal implications, it is a moral duty to safeguard natural ecosystems from the detrimental effects of this hazardous substance.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve into the specific guidelines and ethical practices related to used oil disposal, shedding light on environmentally friendly alternatives and legal compliance. By understanding and adhering to these considerations, car owners can contribute to the preservation of both legal integrity and ecological balance.
Oil Change Process
Embarking on the journey of an oil change involves a systematic process that not only ensures the longevity of the vehicle but also demands careful adherence to environmental and legal protocols. Here is an expanded insight into the comprehensive oil change process:
- Choosing an Appropriate Location:
Selecting the right location for an oil change is the first crucial step. Legal regulations explicitly forbid this operation in public spaces, necessitating a private and designated area. Options include a personal garage or a friend’s facility, ensuring a controlled environment to mitigate the risk of spills. - Preventing environmental contamination:
Before initiating the oil change, it is imperative to recognize the environmental impact of oil spills. Engine oil is a hazardous substance that can contaminate soil and water. Careful handling, such as using oil-absorbent materials and having a proper disposal strategy, is essential to prevent adverse environmental effects. - Proper disposal of used oil:
The responsibility doesn’t end with the oil change; the disposal of used oil demands equal attention. Various options exist, including storing the used oil in appropriate containers, returning it to a gas station, or depositing it at a lubricant sales point. Alternatively, specialized stations dedicated to the disposal of such waste can be utilized, ensuring environmentally responsible practices. - Legal Compliance:
Adhering to legal regulations is a cornerstone of the oil change process. Violating laws related to oil change locations or improper disposal can lead to substantial fines. Additionally, the potential loss of a vehicle’s registration certificate underscores the importance of legal compliance in this seemingly routine automotive task. - Consideration of Professional Services:
For those without the necessary space or facilities, engaging a professional workshop for an oil change is a viable option. Reputable workshops are obligated to handle waste disposal responsibly, alleviating the car owner’s concerns about the environmental impact of used oil. - Discouraging Unethical Practices:
The sale of used engine oil has gained popularity, but this practice raises environmental and ethical concerns. Discouraging such transactions is essential, as the improper processing of used oil into illegal and toxic furnace fuel poses significant threats to the environment.
Understanding and meticulously following this oil change process ensures that car owners not only maintain the health of their vehicles but also contribute to a cleaner and ecologically sustainable automotive ecosystem.
Disposal of Used Oil
Proper disposal of used oil is a critical aspect of responsible automotive maintenance, considering its potential environmental impact and legal implications. This section provides an expanded overview of the various facets involved in the disposal of used oil.
- Environmental Considerations:
Used engine oil, laden with contaminants and impurities, poses a significant threat to the environment if not disposed of correctly. Engine oil contains harmful substances such as heavy metals and hydrocarbons, which can seep into the soil and water, causing pollution and ecological damage. Recognizing these environmental risks underscores the importance of adopting ecologically sound disposal practices. - Storage in Appropriate Containers:
A recommended method for handling used oil is to store it in suitable containers. Large metal barrels are preferred for storage, ensuring that the containers are sealed to prevent leaks. Properly containing the used oil facilitates its transport to dedicated disposal points without the risk of spillage. - Returning to a Gas Station:
Gas stations often serve as collection points for used oil. Once the car owner has accumulated a sufficient amount of used oil, returning it to a gas station becomes a convenient and environmentally responsible option. Gas stations typically have mechanisms in place to handle used oil disposal safely. - Utilizing Lubricant Sales Points:
Some lubricant sales points accept used oil from customers, albeit on a voluntary basis. While there is no strict obligation for these stores to take in waste oil, fostering good relationships with the point of purchase can enhance the likelihood of them accepting the used oil. This approach often involves negotiating with the lubricant sales point during the purchase of new engine oil. - Specialized Waste Disposal Stations:
Specialized waste disposal stations dedicated to handling used automotive fluids provide a regulated and environmentally conscious solution. These stations are equipped to manage the proper disposal of used oil, ensuring that it undergoes appropriate treatment and recycling processes. - Professional Workshop Disposal:
Opting for a professional workshop for an oil change provides a straightforward solution to the disposal challenge. Reputable workshops are obligated to manage waste disposal responsibly, alleviating concerns about the environmental impact of used oil. Car owners can rely on the expertise of workshop personnel to handle the disposal process efficiently. - Discouraging Unethical Practices:
A crucial consideration in the disposal of used oil involves discouraging unethical practices such as the sale of used engine oil. This practice, if not regulated, can result in the improper processing of used oil into illegal and toxic furnace fuel, posing severe environmental and health risks.
Understanding the environmental implications, adhering to legal regulations, and choosing responsible disposal methods collectively contribute to a sustainable approach to managing used engine oil. Car owners play a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of used oil on the environment by adopting conscientious disposal practices.
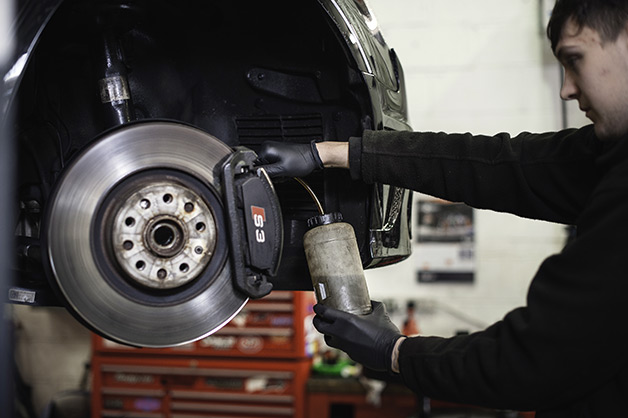
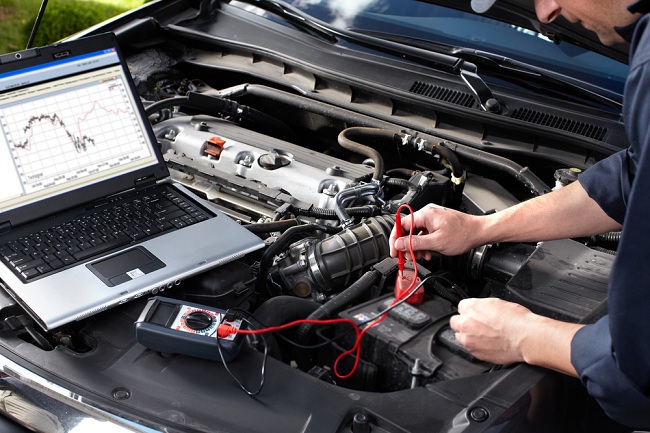
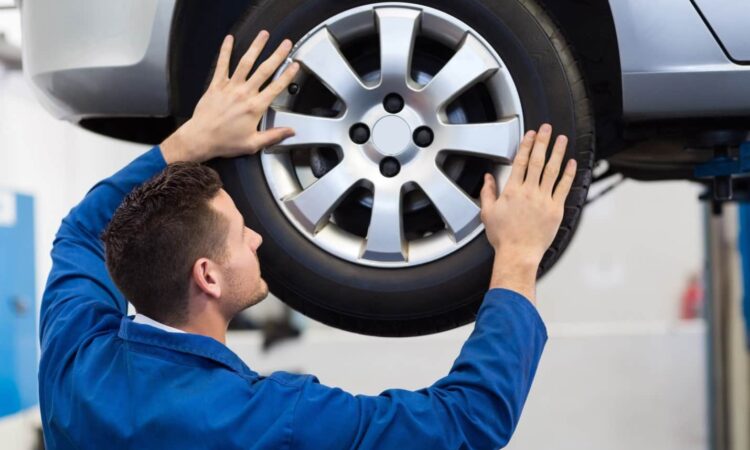
Oil Change in the Workshop
When it comes to changing engine oil, seeking professional services at a workshop offers a convenient and environmentally responsible solution. This section delves into the details of the oil change process when conducted in a workshop:
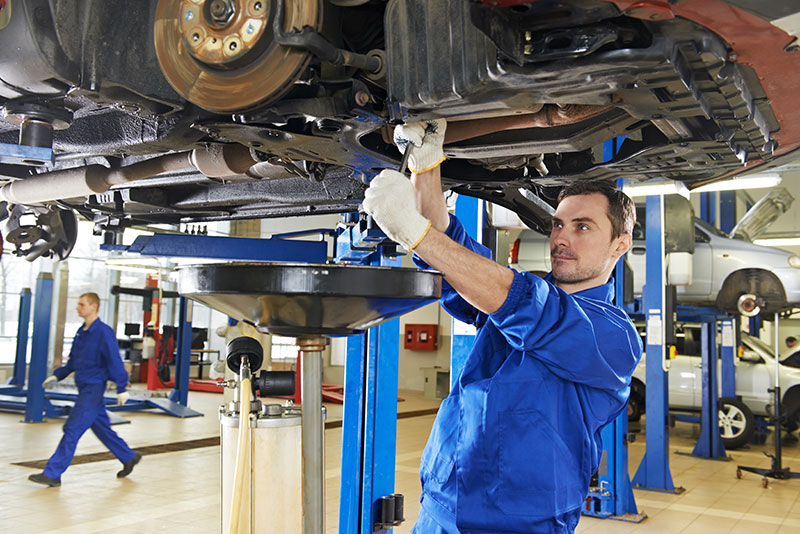

- Professional Expertise:
Opting for an oil change in a workshop ensures that the process is executed by trained professionals. Qualified mechanics possess the expertise to perform oil changes efficiently, minimizing the likelihood of spills or environmental contamination. - Comprehensive Inspection:
Workshops not only handle the oil change itself but also conduct a comprehensive inspection of the vehicle. This includes assessing the condition of the oil filter, checking for potential leaks, and inspecting other vital components. This proactive approach aids in identifying any emerging issues before they escalate. - Proper waste management:
A key advantage of having an oil change at a workshop is the assurance of proper waste management. Reputable workshops are equipped to handle the disposal of used oil and other waste materials in accordance with environmental regulations. Car owners can trust that the workshop staff will manage the entire process responsibly. - Adherence to Environmental Standards:
Professional workshops operate within established environmental standards and regulations. This commitment ensures that the disposal of used oil aligns with eco-friendly practices. The workshop’s adherence to environmental standards contributes to a collective effort to minimize the ecological impact of automotive maintenance activities. - Efficient Recycling Processes:
Workshops often collaborate with recycling facilities for the proper treatment of used engine oil. Recycling processes can reclaim valuable components from the used oil, promoting sustainability by reducing the need for raw materials in lubricant production. This commitment to recycling aligns with broader environmental conservation goals. - Customer Convenience:
Choosing a workshop for an oil change provides customers with a hassle-free experience. Car owners can delegate the oil change task to professionals, saving time and effort. Additionally, workshops are well-equipped to handle the entire process, from draining the used oil to refilling the engine with fresh, high-quality oil. - Legal Compliance:
Workshops are obligated to comply with legal regulations regarding waste disposal. This includes used oil, filters, and other materials generated during the oil change process. Car owners can have confidence in the workshop’s commitment to meeting legal standards, ensuring that the environmental impact is minimized. - Documentation for Accountability:
Professional workshops often maintain documentation related to waste disposal activities. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance with environmental regulations. Car owners can request information about the workshop’s waste management practices, promoting transparency and accountability.
Choosing a workshop for an oil change not only ensures optimal engine performance but also aligns with responsible environmental practices. The combination of professional expertise, proper waste management, and adherence to environmental standards makes the workshop oil change option a reliable and sustainable choice for car owners.
Risks of Illegal Oil Disposal
Illegal oil disposal poses significant risks to the environment, public health, and regulatory compliance. This section explores the multifaceted dangers associated with improper handling of used engine oil.
- Environmental Contamination:
- Soil Pollution: Discarding used oil irresponsibly, such as by by pouring it onto the ground or into drains, can lead to soil contamination. The toxic compounds present in oil can penetrate the soil, affecting its fertility and composition.
- Water Contamination: Perhaps the most severe consequence is the contamination of water sources. Used oil contains hazardous substances that can leach into groundwater, rivers, or lakes, posing a serious threat to aquatic ecosystems and the communities relying on these water bodies.
- Impact on Wildlife:
- Aquatic Life: Water bodies contaminated with used oil can have detrimental effects on aquatic life. Fish, birds, and other organisms may suffer from toxic exposure, leading to population decline and disruptions in the natural balance of ecosystems.
- Terrestrial Wildlife: Soil contamination can also affect animals and plants in terrestrial ecosystems. Creatures relying on contaminated areas for habitat or food sources may experience adverse health effects.
- Air Pollution:
- Combustion Emissions: Improper burning of used oil, a common illegal disposal method, releases harmful pollutants into the air. The combustion process generates air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and respiratory issues.
- Legal Consequences:
- Fines and Penalties: Engaging in illegal oil disposal practices can result in significant legal consequences. Regulatory authorities impose fines and penalties on individuals or businesses found guilty of violating environmental laws. These financial repercussions can be substantial and may vary depending on the severity of the violation.
- Community Health Hazards:
- Exposure Risks: The release of toxic substances from improperly disposed oil can pose health risks to nearby communities. Inhalation of fumes, ingestion of contaminated water or food, and direct contact with polluted soil may lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems, skin disorders, and more.
- Ecosystem Disruption:
- Biodiversity Impact: Contamination from used oil disrupts ecosystems by negatively impacting biodiversity. Indigenous species may struggle to survive, and invasive species that thrive in polluted environments may proliferate, further destabilizing ecosystems.
- Long-Term Environmental Damage:
- Persistent Effects: The environmental damage caused by illegal oil disposal can persist for extended periods. Even small quantities of oil can have long-term consequences, affecting landscapes and ecosystems for years or decades.
- Community Awareness and Perception:
- Public Perception: Communities are increasingly aware of environmental issues, and incidents of illegal oil disposal can damage the reputation of individuals or businesses involved. Public perception matters, and being associated with environmentally harmful practices can lead to a a loss of trust and credibility.
Understanding the risks associated with illegal oil disposal is crucial for fostering responsible practices. By raising awareness about these risks, regulatory bodies, environmental organizations, and communities can work collaboratively to prevent and address the improper disposal of used engine oil.
FAQ About Oil Change
Q1: Why is it important to change engine oil regularly?
A1: Regular engine oil changes are essential to maintain optimal engine performance and prevent potential damage. It ensures proper lubrication, cooling, and debris removal, extending the life of your vehicle.
Q2: Can I change my engine oil anywhere?
A2: No, changing oil in public areas, like parking lots, is prohibited and may result in fines. It’s recommended to use design spaces, like a garage or a car pit, for environmentally safe oil changes.
Q3: What should I do with used oil after an oil change?
A3: Used oil should be stored in appropriate containers and disposed of at designated collection points, gas stations, or lubricant sales points. Burning used oil on traditional stoves is prohibited and harmful to the environment.
changeQ4: Is it legal for a workshop to refuse my used oil if I change it myself?
changeA4: Yes, workshops may refuse used oil if you change it yourself. It’s advised to consult with the workshop beforehand or use their services for proper disposal.
Q5: Why is illegal oil disposal harmful?
A5: Improper oil disposal harms the environment, leading to pollution of water sources and ecosystems. It can also result in severe legal consequences and fines for violators.
Q6: How can I dispose of used oil responsibly?
A6: Responsibly dispose of used oil by using certified recycling centers, authorized collection points, or returning it to a gas station or lubricant sales point. Following legal and eco-friendly methods ensures proper disposal.
Q7: What are the risks associated with illegal oil disposal?
A7: Risks include environmental damage, health hazards, and legal repercussions. Improperly disposed oil can contaminate soil and water, harm wildlife, and lead to fines or legal actions against individuals or businesses.
Q8: How can communities raise awareness about proper oil disposal?
A8: Communities can organize awareness campaigns, distribute informational materials, and collaborate with local authorities to educate the public about the environmental and legal consequences of improper oil disposal.
Q9: Why is continuous monitoring and enforcement of oil disposal important?
A9: Continuous monitoring and enforcement deter illegal oil disposal, ensuring compliance with environmental laws. Regulatory authorities play a crucial role in preventing and penalizing violations.
Q10: What is the long-term impact of responsible oil disposal on the environment?
A10: Responsible oil disposal contributes to the long-term health of the environment, safeguarding ecosystems, water sources, and air quality. Sustainable practices minimize pollution and support conservation efforts for future generations.
Q11: Are there specific regulations regarding oil disposal in my region?
understand theA11: Yes, regulations vary by region. Check with local environmental agencies or authorities to understand the specific rules and guidelines for oil disposal in your area.
Q12: Can used engine oil be recycled?
reducing itsA12: Yes, used engine oil can be recycled. Many recycling centers and collection points accept used oil for proper recycling, reducing its environmental impact.
Q13: Is it recommended to sell used engine oil?
A13: No, selling used engine oil is not recommended. It can lead to illegal and harmful processing, contributing to environmental pollution. Proper disposal is crucial for environmental protection.
Q14: How often should engine oil be changed?
A14: The frequency of oil changes depends on factors like vehicle type, driving conditions, and oil type. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations or consult with a mechanic for a personalized schedule.
Q15: What are the consequences of not changing engine oil regularly?
A15: Neglecting regular oil changes can lead to increased engine wear, reduced performance, and potential engine damage. It may result in costly repairs and a shorter lifespan for the vehicle.
Q16: Can I dispose of used oil at home?
A16: No, disposing of used oil at home is not recommended. It should be taken to designated collection points or recycling centers to ensure proper and eco-friendly disposal.
Q17: How can workshops contribute to responsible oil disposal?
A17: Workshops can play a vital role by properly collecting, storing, and disposing of used oil in accordance with environmental regulations. Collaboration with certified waste disposal services is essential.
changingQ18: Is DIY oil changing safe for the environment?
A18: Yes, a DIY oil change can be environmentally safe if conducted in designated areas with proper disposal of used oil at authorized collection points.
Q19: What are the benefits of adhering to oil change regulations?
A19: Adhering to oil change regulations promotes environmental conservation, prevents pollution, and ensures the well-being of ecosystems. It also avoids the legal consequences associated with improper disposal.
Q20: How can individuals promote responsible oil disposal in their communities?
A20: Individuals can promote responsible oil disposal by educating others, participating in community clean-up initiatives, and encouraging the use of authorized collection points for used oil.
Q21: How Much Oil Should My Car Be Burning – When Should I Be Concerned?
A201: Basically, the typical car consumes approximately a quart of oil, more or less, every 3000 miles. However, if you observe your car using around a quart of oil within every 1000 miles or less, that’s when you should become alarmed.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of responsible oil disposal is paramount for both environmental preservation and compliance with legal regulations. Whether changing oil at home or in a workshop, adhering to proper disposal methods ensures the prevention of pollution and potential legal repercussions. The careful consideration of regional laws and collaboration with authorized waste disposal services contribute to a collective effort to safeguard our environment. By fostering a culture of responsible oil disposal, we not only protect ecosystems but also contribute to the well-being of our communities.